Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland that affects men aged 20 years and older.
According to statistics, 1 in 4 men have suffered from the disease in one form or another. In recent years, there has been a tendency to "rejuvenate" the process. This is due to sexual liberation, an increase in sexually transmitted infections, the tendency of self -diagnosis and treatment on the Internet, and the resistance of infectious agents to the action of antibiotic therapy.
This is especially true because the first signs of prostatitis in men, as a rule, are pronounced erased, which makes it impossible to see a doctor in time and in some cases leads to the development of further prostatitis.
Signs of prostatitis in men
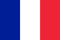
The structural features, blood supply and location of the prostate gland influence the nature of the symptoms that will cause its inflammation. This includes:
- Symptoms of pain.
- Symptoms of urinary disorders (excreted).
- Symptoms of erectile dysfunction.
Symptoms of pain
Sensation of pain, of varying intensity, bothers men in the lower abdomen, in the perineum, genitals, lumbosacral spine. The location of this pain is due to the presence of nerve connections and the involvement of seminal vesicles (vesicles) in the inflammatory process.
Pain can vary in intensity, from unexplained discomfort to intense pain that affects a man’s mental state and causes insomnia. Painful sensations depend on sexual behavior and arise as a result of lack of normal ejaculation or, conversely, with ejaculation, which is associated with the spread of inflammatory processes in the posterior urethra.
Note that pain in the lumbosacral area may not be related to the prostate gland in any way, but may be the result of, for example, spinal osteochondrosis. The results of conversations with patients and urological examination data help determine the cause of the pain.
The first sign of prostatitis in a man is a sensation of pain in the testicles (in the scrotal area) with spread along the epididymis (right and left groin area). Pain radiating from an inflamed prostate can appear in the inner thighs, buttocks, which determines the need to consult a neurologist to exclude neurological pathology, because precisely for such diffuse prostate pain is not typical.
In some cases, the irradiation of painful sensations is asymmetric, which makes it possible to suspect an inflammatory process in the prostate, which is localized in one of its lobes. At the site of manifestation, the pain syndrome is divided into genital (in the genital area, characteristic of chronic congestive prostatitis), extragenital (above the genital organs), characteristic of advanced prostatitis) and mixed (chronic prostatitis).
Symptoms of dysuria or urinary disorders with prostatitis
Urinary disorders are expressed by false desire, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder with frequent urination, which is associated with inflammation in the neck of the bladder and urethra. Signs of chronic dysuria in prostatitis indicate chronicity of the process.
Erectile dysfunction with prostatitis

Erectile dysfunction in prostatitis is represented by premature ejaculation, blurred sensations during orgasm, decreased libido, weak erections. Sometimes male prostatitis can be suspected by the absence of a morning erection.
Decreased potency, as the first sign of prostatitis in a man, is caused by a decrease in the synthesis of testosterone (male sex hormone).
The manifestation of inflammation in the prostate gland is not limited to the above three symptoms. Often the first sign of prostatitis in a man is the release of prostate secretions from the urethra during defecation (prostatorrhea), which indicates a decrease in the tone of the muscles of the ejaculatory tract.
In addition, one should not focus on the psychological signs of prostatitis in a man: astheno-neurotic syndrome develops from the nervous system (depression, fatigue, lack of desire to do anything, physical weakness)
The first signs of acute prostatitis
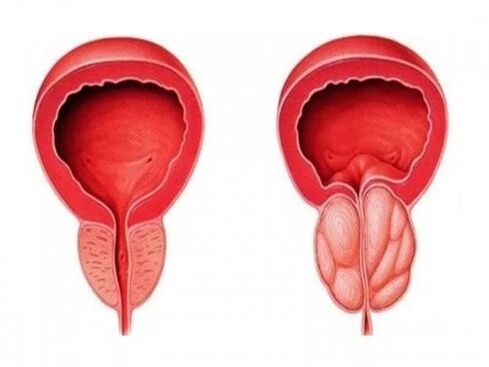
All of the above symptoms are typical for chronic inflammation of the prostate, with acute prostatitis in a man, the picture is quite different.
The disease begins with severe pain in the perineum, symptoms of urinary disorders are more clearly detected. There is an increase in temperature to 38-39 C, chills, weakness, sweating, pain in muscles and bones. During defecation, the pain in the anus is worrisome. There is no sex life.
If you do not pass a timely examination and do not begin treatment, then the acute process will be complicated by purulent prostatitis, to abscesses, which will lead to emergency surgery.
If there is no other cause (immunodeficiency condition, severe concomitant pathology, etc. ) - purulent prostatitis in a man - an advanced inflammatory process due to timely access to a doctor!
Causes of symptoms of prostate inflammation
Factors influencing inflammation of the prostate are conventionally divided into 3 groups.
Unresponsive factors include:
- Body type.
- Sexual constitution.
- Age factor.
- The presence of disease.
- Environment (climate factors).
Partially controlled factors:
- Sexual habits.
- Profession.
- Background of the disease in the male genital area.
- Attitudes towards this disease.
And finally, the factors that can be controlled:
- A tapered sex life.
- Alcohol addiction.
- Non -compliance with treatment recommendations.
- Fault in power supply mode.
Who is at risk
Prostatitis threatens men who:
- Adhere to an inactive lifestyle.
- Suffering from chronic constipation.
- Have a history of venereal infection.
- Having more than one sexual partner.
- Suffering from alcoholism, drug addiction.
- They work in the cold.
If there are signs of prostatitis, what to do
Laboratory diagnostics for prostatitis

- In KLA, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases, the leukocyte formula shifts to the left. In OAM - leukocyturia, proteinuria, bacteria.
- Blood for HIV infection.
- Smear from the urethra on the flora. As a rule, on smears, leukocytes completely. If venereal pathogens (Neisser gonococcus, Trichomonas) are not identified, it is important to perform PCR diagnostics.
- Prostate secretion Inhibition of prostate secretion on pathogens and determination of sensitivity to antibiotics.
- PCR - diagnostic for sexually transmitted infections. The most reliable and fastest method for confirming pathogens.
- Blood for PSA Blood for PSA (prostate -specific antigen) should not be taken during the acute inflammatory process of the prostate gland, the results are unreliable. It is best to perform this analysis 1 month after the end of therapy. Young people under the age of 30 do not need to check PSA levels in the blood. This test is important for men over the age of 40, because acute prostatitis, in some cases, can be secondary, and malignant tumors of the prostate gland are covered behind its clinical manifestations.
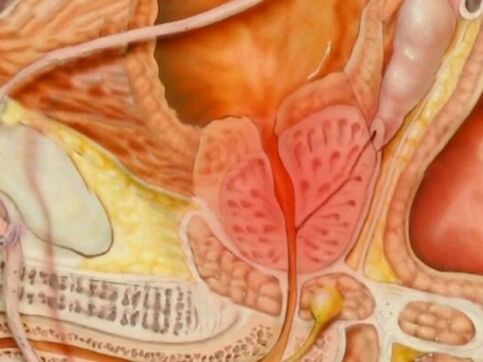
Instrumental diagnostic methods
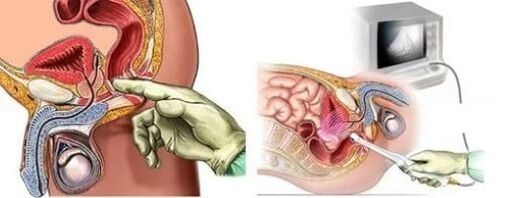
As a rule, ultrasound examination of the prostate transrectally (through the rectum) or transabdominally (through the abdomen) is sufficient.
Signs of prostatitis on ultrasound
Increased gland volume, changes in texture, edema; with purulent prostatitis - areas of necrosis, contour deformation, enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
What you should pay attention to
First of all, to get rid of the symptoms of prostatitis forever, you must follow a certain diet.
Exacerbation of prostatitis in men depends on the irritating substances consumed with food: hot spices, vinegar, pickles, alcohol.
Special attention should be paid to alcohol, even its minimal use can cancel out the long -term effects of complex therapy.
Some patients feel that they should drink less or switch to lighter alcoholic beverages. This is their main mistake.
Liquid vinegar, kvass, citrus fruits, sauerkraut, tomatoes and cucumbers have no harmful effects on prostatitis.
Eating foods rich in fiber will relieve constipation - one of the main reasons for the development of congestion in the small pelvis.
Herbal medicine helps prevention. Taking herbal diuretics: lingonberry leaves, dill seeds, urological accumulation helps to increase urination during the inflammatory process.
Exercise, especially exercise to increase blood circulation in the pelvic organs, helps keep the prostate in good condition.
The development of inflammation in the prostate gives rise to hypothermia. In the winter, you need to dress warmer, and in the summer, after swimming, you should not be in wet swimming trunks for long periods of time.
Using a condom during sexual intercourse with an unfamiliar partner will protect you from sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV infection.
Prolonged fatigue has a negative effect on the male immune system, as well as stressful situations, which can exacerbate an inactive infection of the prostate gland. Regular preventive checkups by a urologist will help keep men healthy.